Osmium
Osmium (British: osmium) is an element of atomic number 76. The symbol of an element is Os. One of the platinoid elements (a noble metal).
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Bluish silver-white | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General characteristic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name, Sign, Number | Osmium, Os, 76 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Classification | Transition metal | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Family, Period, Block | 8, 6, d | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic weight | 190.23 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Xe] 4f14 5d6 6s2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
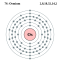
| Electron shell | 2, 8, 18, 32, 14, 2(Image) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical characteristic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aspect | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (room temperature neighborhood) | 22.59 [1] g/cm3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Liquid density at the melting point | 20 g/cm3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | 3306 K, 3,033 degrees Celsius, 5,491 degrees Fahrenheit | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The boiling point | 5285 K, 5,012 degrees Celsius, 9,054 degrees Fahrenheit | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | 57.85 kJ/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The heat of evaporation | 738 kJ/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal capacity | (25 degrees Celsius) 24.7 J/(mol·K) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atom properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation state | 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, -1, -2 (acidulous oxide) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronegativity | 2.2 (value of the polling) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energy | The first: 840 kJ/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The second: 1600 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Zirconium | 135 pm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 144+-4 pm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal structure | Hexagonal system | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetism | Paramagnetic [2] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electric specific resistance | (0 degrees Celsius) 81.2 nΩ·m | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal conductivity | (300 K) 87.6 W/(m·K) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal expansion rate | (25 degrees Celsius) 5.1µm/(m·K) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The speed to come of the sound (minute rod) | (20 degrees Celsius) 4,940m/s | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rigidity | 222 GPa | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Volume coefficient of elasticity | 462 GPa | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Poisson ratio | 0.25 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mohs scale | 7.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The yellowtail flannel hardness | 3920 MPa | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS registration number | 7440-04-2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The most stable isotope | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The details refer to an isotope of osmium | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table of contents
Summary
The metal (transition metal) specific gravity of the blue gray 22.57, the melting point 3,045 degrees Celsius (there is the experimental value of 2,700 degrees Celsius, too). The boiling point exceeds 5,000 degrees Celsius. The crystal structure that is stable by normal temperature, ordinary pressure is hexagonal close-packed structure structure (HCP). The specific gravity is the biggest among all elements (as for iridium the second).
I can take the oxidation state to +1-+8 value (+4 value becomes stable most). It is easy to be oxidized most in platinum group. I react at a high temperature with halogen, but do not dissolve in aqua regia very much. It is a rare metal (rare metal).
When I leave you unattended in the air or the powder heats up, I produce oxidation osmium (VIII) of the deadly poison easily.
It is the element which is the highest in density [1].
History
In 1803, I was discovered in an aqua regia dissolution residual substance of rough platinum with iridium by a British tenant (Smithson Tennant, 1761-1815). Because the osmic acid which occurred when I heated up gave off a special smell, I was named for ο σ μ η (osmè, smell) of the Greek.
Use as the material
It is corrosion-resistant firmly, and the alloy with platinum and iridium is superior, and the alloy with iridium to produce particularly naturally is called osmiridium and iridosmine which content is high. I am used for the pen point of the fountain pen and produce a lot it in Hokkaido in Japan. In addition, I use a property that oxidation osmium and organic matter perform a reaction (reduction) and produce an osmium simple substance (black) and may be used for the fingerprint detection.
Compound of osmium
- Oxidation osmium (IV) (OsO2)
- Oxidation osmium (VIII) (OsO4) - I am catalyzed, but am toxic
Isotope
Gallery
Source
- In ^ a b Theodore gray "element illustrated book Mari Takei reason which is the most beautiful in the world", wound former company, 2010, it is 177 pages
- ^ Magnetic susceptibility of the elements and inorganic compounds, in Handbook of Chemistry and Physics 81st edition, CRC press.
Outside link
- Osmium Niihama National College of Technology
This article is taken from the Japanese Wikipedia Osmium
This article is distributed by cc-by-sa or GFDL license in accordance with the provisions of Wikipedia.
In addition, Tranpedia is simply not responsible for any show is only by translating the writings of foreign licenses that are compatible with CC-BY-SA license information.
0 개의 댓글:
댓글 쓰기