Photolithography

A technique to generate the pattern consisting of the part which photolithography (British: Photolithography) is to perform exposure (I say pattern exposure, the image-like exposure) of the surface of the material which applied a photosensitive material into a pattern form, and was exposed and the parts which are not exposed. I am used for production such as a semiconductor element, a printed circuit board, a printing plate, a liquid crystal display panel, the plasma display panel mainly.
Table of contents
Production of the semiconductor element
The photolithography is performed in the production of the semiconductor element as follows. I apply the photosensitive organic substance called the photoresist on the semiconductor wafers such as silicon, the gallium arsenide and, using exposure equipment called ステッパー, print the pattern of an element, the circuit drawn on the photomask called レチクル. I explain a process in detail as follows.
Coat
I stop by to spray spin Coe terや and, on the silicon wafer, apply the liquid called the cash register strike. The cash register strike dissolved a chemical substance reacting by light in a solvent, and "a positive type" and a part exposed to light which a part exposed to light dissolves are left, and there is "a negative type". It is said that a positive type is advantageous to the miniaturization of the pattern, and a positive type is mainstream now. In addition, in the case of exposure using excimer laser such as KrF, a chemical amplification model photoresist is used because exposure strength is weak.
Prebake
I heat the wafer which applied a cash register strike and solidify a cash register strike.
Exposure
I irradiate a cash register strike with light and react it. Using the mask which I drew the shape of the connection diagram on then, I describe a necessary shape on the cash register strike by controlling the part which irradiates it with light. The exposure equipment was ever exposure to let a mask and a wafer adhere, and to expose it, and to double, but changed in technique to expose a reduction projection while moving the mask pattern that in late years I more greatly than an exact size made over a wafer using a device called ステッパー because a required pattern became minute, and the making of the mask became difficult. The source of light of the short wavelength is necessary so that a pattern reduces it, and the g line (wavelength 436nm) of the high-pressure mercury-vapor lamp, i line (wavelength 365nm), KrF excimer laser (wavelength 248nm), ArF excimer laser (wavelength 193nm) are mainstream now, and EUV light (wavelength 13.5nm:EUV lithography) is under development as a next-generation source of light. In addition, I use X-rays for a source of light, and the method (electron beam lithography) to paint pictures on the direct cash register strike in an electron beam exists.
The developing, conditioner
I soak the wafer which I exposed into developing solution and remove the cash register strike of the extra part. The pattern of the connection diagram appears on the wafer for the first time in this process. As for the developing solution, medicinal solution dissolving a cash register strike is used. In the case of an organic solvent dissolving a cash register strike to used medicinal solution, I may be the organic or inorganic alkali. By the photolithography for the current semiconductor, a 2.38% by weight water solution of TMAH (Tetra-methyl-ammonium-hydroxyde) which is organic alkali becomes mainstream. This is because the mixture to the process of metal ions is not avoided by the inorganic alkali such as potassium hydroxide (KOH). I completely remove a rinse, an unnecessary part with conditioner liquid (mainly super pure water) several times.
Post-baking
I remove the conditioner liquid which attached by heating. By heating, the coherency with the wafer improves.
Pattern molding
I make desired circuits using a drawn pattern by a cash register strike. A process varies according to the thing which I used for a wafer, and it is the process of film formation, the liftoff when I want to add the circuit which is necessary by etching when I want to remove an unnecessary part.
Etching
When they want to add merely irregularity to a wafer or originally the cases that a pattern was made on the wafer remove an unnecessary part by etching. Dry etching and wet etching exist. Because the left part of the cash register strike is not removed by etching, the pattern that I want to leave is formed on the wafer. Finally I completely remove a cash register strike by solvents.
Film formation, liftoff
When I want to attach different metal or oxide on the wafer, I form a film by technique such as vacuum deposition and sputtering, the CVD. Finally when remove a cash register strike with solvents, the materials layered on the cash register strike are removed at the same time (it is said with a liftoff); save it, and can add a favorite pattern on the wafer.
Resolving power in the exposure system
The resolving power depends on the wavelength of the source of light to use in a reduction exposure system. It is decided whether you can expose it by the performance of the reducing glass to the diffraction limited of the mask. When I use a violet outside line of wavelength 248-193nm, I can expose it to linewidth of 50nm.
The pro-exposure smallest linewidth is found in the following expressions:
Here, the definitions of each fixed number and variable are as follows:
 は 最小線幅 (generally called the aim design rule). The number of times in 2 half pace to usually multiply by 2
は 最小線幅 (generally called the aim design rule). The number of times in 2 half pace to usually multiply by 2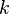 Coefficient (usually similar in 0.5) that (generally called the k1 factor) expresses the factor in conjunction with the process
Coefficient (usually similar in 0.5) that (generally called the k1 factor) expresses the factor in conjunction with the process Wavelength of the は source of light
Wavelength of the は source of light Opening rate for the は wafer
Opening rate for the は wafer
The smallest linewidth depends on the opening rate at the same time to depend on the wavelength. If an opening rate becomes big, the lens grows big and accesses a wafer. I check these elements each other. I am as follows now [the source required]:
The depth of field is influenced by the sectional thickness of the photoresist. It is necessary to improve the appearance of the wafer by chemical abrasion as a premise to get high resolution flatly, and to raise a plane degree.
Production of the printing plate
A pattern exposes the board which applied a photosensitive material and it is for a flexo and can make the printing plate first edition such as planography, the waterless planography by developing it, and removing an unnecessary part. I connect exposure equipment to a computer editing an inked surface, and a computer toe plate (Computer to Plate, CTP) means that I make the direct printing plate first edition. In addition, I call the aluminum board which applied a photosensitive material beforehand used for making for surface printing a PS version (pre-sensitised plate). Because the plate-making process from from the manuscript including a photograph and the picture or an electronic medium is easy, the PS versions spread widely.
Origin of the name
As for the photolithography (Photolithography), technique (Lithography) to incise an image pattern on a board (including a picture and the letter) means using a photograph (Photo) technique. "リソ" (litho) is the will of the stone and I incise a picture on slate and am the concept that is the same as 刷版 of the monotonous print and a lithograph (Lithograph) doing it, but a point acid-treating the board surface as a mask in the part which remained is different in the developing of the photoresist by the photo lithography whereas I acid-treat the board surface of the non-drawing region as a mask, and the lithograph hydrophilizes the paint which a painter describes in slate directly. In addition, in the field of print, it is the last process before the print to make 刷版 by photolithography, but is only one (but it is important) technique used every process of the number that is enormous in the field of semiconductor. In addition, it reads "Lithograph" meaning a lithograph with "a lithograph" in Japan, and it is common to read "Lithography" in the field of semiconductor with "lithography". Because it supplied a photoresist in one Kodak Corporation, I was called KPR (Kodak Photo Resist) process and was called PEP (Photo Engraving Process) once. The photolithography and PEP technology is translated as "写真蝕刻" technique in Japanese. Because I am used to print the images such as photographs in the field of print, there is not a sense of incongruity, but is often translated with "光蝕刻" technique, "light lithography" because a sense of incongruity is big in the field of semiconductor which does not use a photograph image for photomask. In addition, in the field of print, it is apt to be misled into thinking that it is a "phototype process" technique because it is a technique to print a photograph, but because it is "a (I make 刷版) to make a plate using a photograph technology" ための technology definitely, it is "a phototype process", and, as for this, "photocomposition" comes from a technique (abbreviated to "photocomposition").
Allied item
This article is taken from the Japanese Wikipedia Photolithography
This article is distributed by cc-by-sa or GFDL license in accordance with the provisions of Wikipedia.
In addition, Tranpedia is simply not responsible for any show is only by translating the writings of foreign licenses that are compatible with CC-BY-SA license information.



0 개의 댓글:
댓글 쓰기